PSEUDOGYNECOMASTIA – represents the increase in breast volume in men caused by the dramatic increase in subcutaneous adipose tissue which is most often a consequence of excessive weight gain. Adipose tissue is frequently located in this area. The breasts have a fat, flattened appearance at the palpation are generally more comparable to the breasts from a true gynecomastia. It is more a consequence of unhealthy, wrong food habits, of sedentarism, than excessive hormonal secretion. If skin elasticity allows, liposuction should be the first choice treatment.
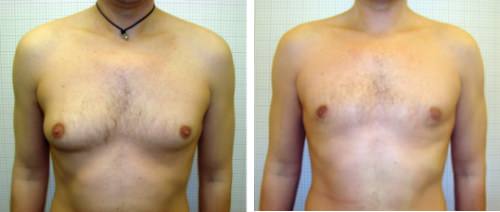
MIXT FORM – represents the form in which the patient shows a growth in the breast size of both glandular and adipose tissue. In most subjects in this category, the clinical examination reveals a slight hypertrophy of mammary gall-duct while adipose tissue claims the “lion’s share”.
In this case, only liposuction should be sufficient, possibly removing glandular tissue residues if necessary. Even if the glandular tissue dominates, it is good to make the aspiration of the fat, then the resection of excess glandular tissue, which can be easier to isolate and remove.
Patients using surgery to solve these problems have both aesthetic and psychological motivation, with dysfunctions then taking their weight in their motivations.
The majority of patients who seek the esthetician’s help with this type of situation are adolescents who find this strange effeminacy of the body during puberty, but men of all ages lament their strange appearance because of such a condition when they look at themselves or when they are observed by strangers.
Breasts can increase their volume at any time in their lives.
Physiological gynecomastia in newborns and infants is rare, can be resolved within a few weeks and is linked to estrogen that is assimilated from breast milk or placenta.
Gynecomastia in adolescence, most commonly occurs around 14 years of age and normally disappears after a few months; there are situations in which they train up to 20 years, leaving behind remnants, sometimes unilaterally.
True gynecomastia with a hypertrophy of mammary gland is probably more likely to be diagnosed in the young population, whereas the older population predominates in adipose tissue; although it can also be found here the mammary gland hypertrophy resulting from the reduction in androgen hormone secretion.
Differential diagnosis consists of palpation, medical history, but can be easily confirmed by ultrasound scanning.
Diagnosis is very important to plan the proper case resolution procedure.
When the breast is largely fat, it will be easy to solve by mastectomy. Of course the mixed form of these conditions involves solving the situation through both maneuvers during the same procedure.
CAUSES: As we have already shown, an important cause is excessive weight gain, reaching obesity or not.
But true gynecomastia may also occur with breast tissue hypertrophy.
The origin of these changes has not yet been fully clarified, but it is surely due to hormonal disturbances. An increase in estrogen secretion can be proven at any time as well as a sensible increase in hormonal levels in breast tissue.
Other causes may be congenital problems that lead to hormonal disturbances, KLINEFELTER syndrome, gonadal tumors, liver disease, thyroid, malnutrition, etc.
It is known that many drugs can cause endocrine disorders that can underpin gynecomastia.
TREATMENT:
PHYSIOLOGICAL GYNECOMASTIA IN CHILDREN, NEONATES AND ADOLESCENTS TENDS TO HEAL SPONTANEOUSLY WITHOUT THE NEED FOR THERAPY.
A large number of cases of drug-induced gynecomastia regress shortly after cessation of treatment with this kind of medication. Pseudogynecomastia can be treated by diet, exercise or liposuction. Gynecomastia due to the growth of glandular breast tissue can be treated with anti-estrogen medication. The possibility of tumor appearance is considered. Attempts to solve these drug problems have not yet been sufficient, the only effective method being the surgical procedure by mastectomy.